Modernisierung ganz easy für IBM z, IBM i und andere

Webswing is a specialized web server for running Swing-based Java applications in your browser.
For many years, Swing has been the framework of choice for many organizations to create large-scale applications that have been heavily invested in development.
The Swing framework is increasingly the limiting factor for development as these applications cannot easily be used in modern web browsers.
The deprecation of applet technology leaves these companies with very few options.
At this point, the Webswing solution offers a way to resolve the restrictions.
With minimal effort, access to a Swing application or applet can be provided immediately in a web browser, just like a native web application.
Activation only requires a simple configuration via the integrated admin web interface.
Important features:
-
- A browser is all you need to run the Java application.
No more installation – just a click on your URL! - No source code changes – install your own Java libraries, configure the location and Webswing will do the rest!
Remember, if it works with Swing, it will work with Webswing! - Migration Framework – a tool for step-by-step migration from desktop to web applications.
The most sensible way to migrate your legacy application currently available on the market. - Cluster Engine – Highly scalable performance and load balancing functions for enterprise customers.
- 100% identical look and feel – your application always looks the same, regardless of whether it is run in desktop mode or via your web browser.
- Test Tool & QF-Test – Ensuring stable performance and smooth running of the Swing application.
Integration with QF-Test for highly stable and easy to maintain test cases. - All browsers are supported – Webswing is supported by all major web browsers that implement the HTML5 standard.
- Embeddable JS snippet – Integrate your application directly into your existing website.
Simply copy the JavaScript snippet and
and paste it directly from our documentation. - Printing in Webswing is seamless.
Simply press the print button and Webswing displays your printed document in your browser.
- A browser is all you need to run the Java application.
Who is it for?
Webswing is designed for existing Swing applications and applets.
If you have a Swing application that you want to deploy in the cloud or as SaaS, or if you are looking for a way to support your applet on modern browsers, Webswing is a great option for you.
Running your application in Webswing has many advantages over standard desktop use, such as
-
- Protection of the codebase of Swing applications
- Simple distribution of a new application version
- Control of the Java version used for the execution of Swing applications No security risks due to outdated Java runtime environment on client computers
- Faster connection to backend services Centralized access management
How does it work?
The Swing API is designed to be cross-platform, i.e. all interactions with platform-dependent functions take place via a clearly defined minimal interface (java.awt.Toolkit).
Java is delivered with platform-specific implementations for Windows, X11 and Mac.
Client Desktop
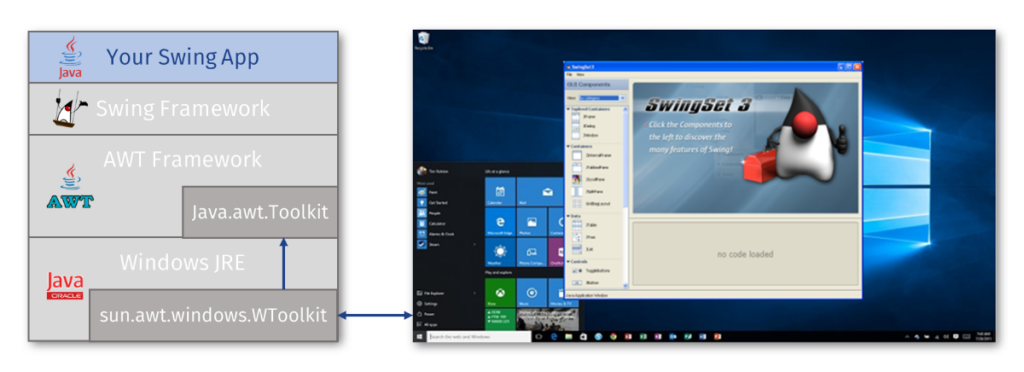
Webswing defines a new platform implementation for “Web” that simply transforms the web browser into a virtual desktop and converts platform-specific actions into browser actions in the best possible way.
Server Side VS Client Side

There are two central actions that every platform must provide for Swing.
-
- Display content on the screen
- Generation of user input events
Webswing displays the content in a browser with HTML canvas and captures keyboard and mouse events in JavaScript to generate Swing input events.
Which functions are supported?
Webswing offers many practical integrated functions that make working with Webswing applications as easy as if they were running locally.
-
- Print integration with preview
- Integration of the file system – downloading / uploading / deleting files in isolated folders
- Extended clipboard integration
- JsLink – JavaScript to Java calls and vice versa
- Embeddable JavaScript – embed Webswing into your website
- Integrated option for session recording and playback
- DirectDraw – Rendering directly from Java2d to HTML Canvas
- Configurable swing window customization options
- Support for Java 8, 11, 17 and 21
- Open JDK
On the server you can:
-
- Configure and monitor your applications via the Admin Console
- Use multi-tenant deployment with isolated login contexts
- Use an integrated security provider (including SAML2 or OpenID Connect) or create your own
- Mirror view – see in the Adminconsole what users see in the browser
- Use your own branding
- Cluster provisioning (Enterprise Edition)
- Docker and Kubernetes (Enterprise Edition)
Network diagram
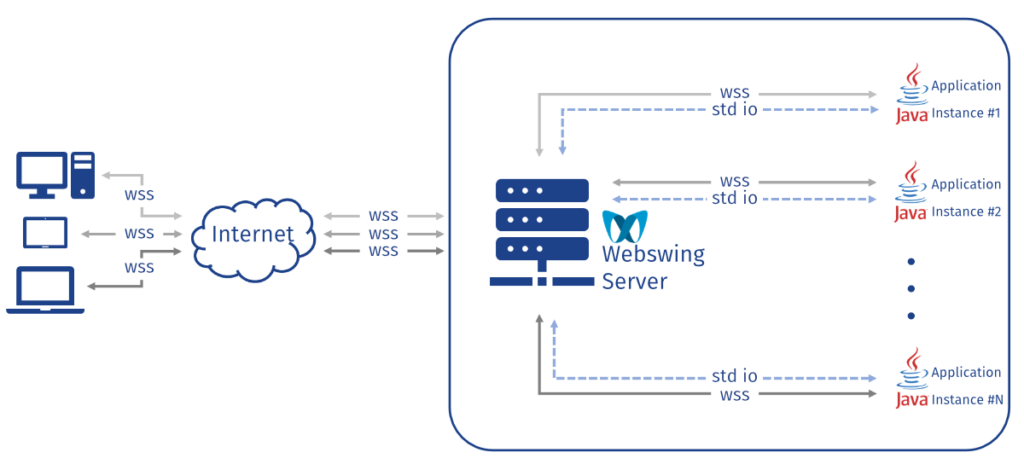
This section describes the network diagram for a standalone webswing in which a client, represented by a browser, communicates with a server.
The server is responsible for the transfer of rendering data from an application to the browser, as well as for the transfer of user events from the browser to the application.
Application: This component is usually a Swing application that runs in its own JVM and is started by the server.
It generates rendering data that must be transferred to the browser and receives user events from the browser.
Webswing server: This component acts as an intermediary between the application and the browser.
It starts the application, establishes WebSocket connections, receives rendering data from the application and transfers it to the browser.
It also receives user events from the browser and forwards them to the application.
The Webswing server can run on a local machine, on-premise, in the cloud or even as a container in a Docker or Kubernetes environment.
Browser: This component represents the client and is responsible for receiving rendering data from the server, updating the rendering of the application and sending user events to the server.
Communication: Communication between the components takes place via a network using WebSocket as the data transfer protocol.
The following steps describe the communication process:
-
- The application generates the rendering data and sends it to the server.
- The server receives the event and transmits it to the browser via WebSocket.
- The browser receives the result and uses it to update the display of the application.
- The updated rendering is displayed to the user, who can interact with it.
- When the user interacts with the rendering, the browser generates a user event and sends it to the server.
- The server receives the user event and forwards it to the application.
- The application processes the user event and updates its status.
Diagram: The following diagram illustrates the network communication for the system described above:
Network diagram
Why Webswing?
Simple distribution
-
- Easier and faster distribution of a new application version.
- Control over the Java version used to run Swing applications.
- No security risks due to outdated Java runtime environment on client computers.
- Faster connection to
backend services / Centralized access management / No installation on the desktop required.
Highest Confidentiality level
-
- Protection of the codebase of Swing applications.
- Recommended for companies and
organizations with software that contains highly sensitive and strictly confidential information.
(e.g. companies in the healthcare, defence, telecommunications, IT, banking, transport, engineering, insurance, airspace, etc. sectors)
Cost savings
-
- Cost savings compared to current Java licensing (applies to Java 8 since January 2019)
- Saving of programming hours – no changes to the source code.
- Future framework for application migration and support.
